- Isolators
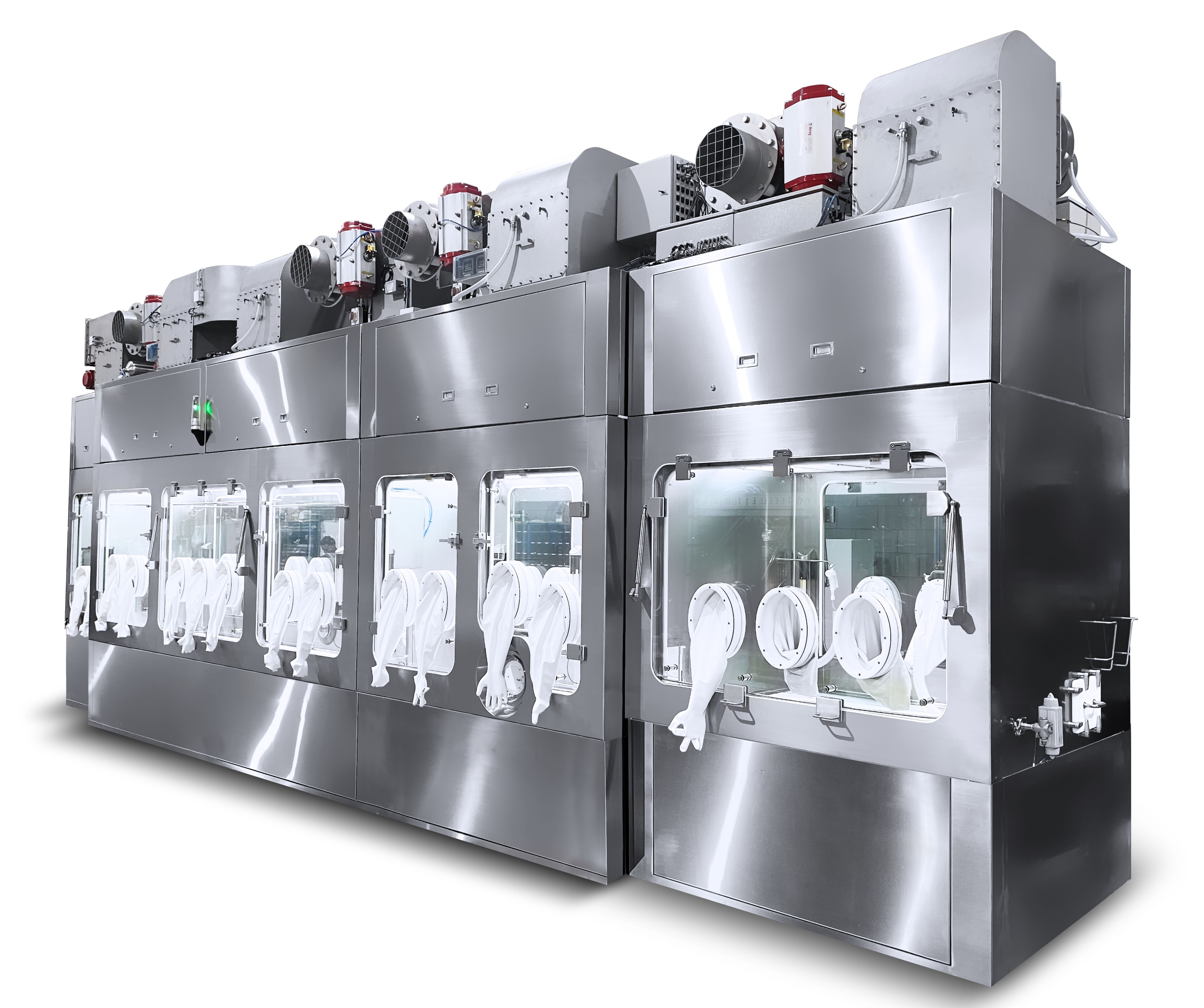
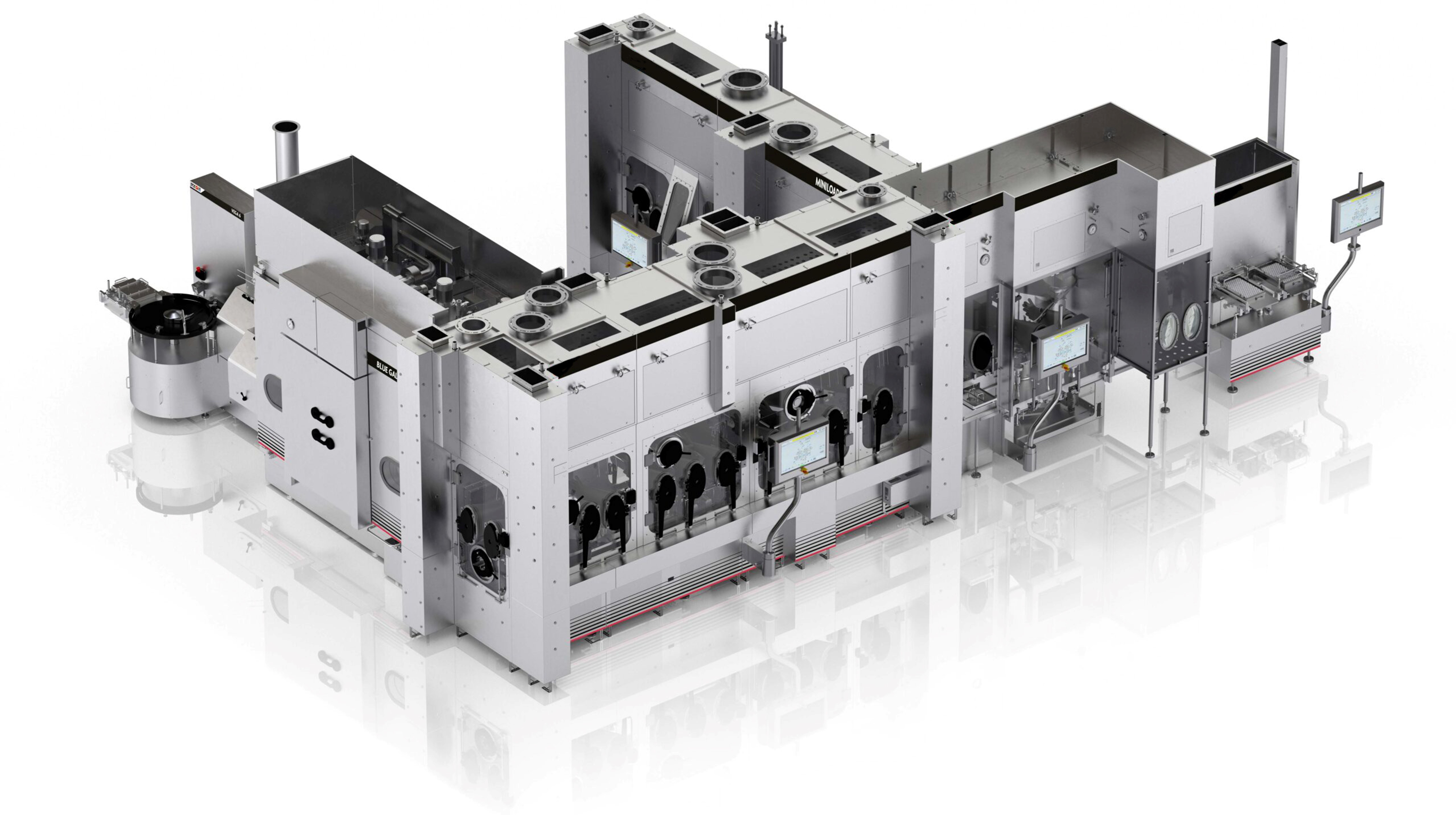
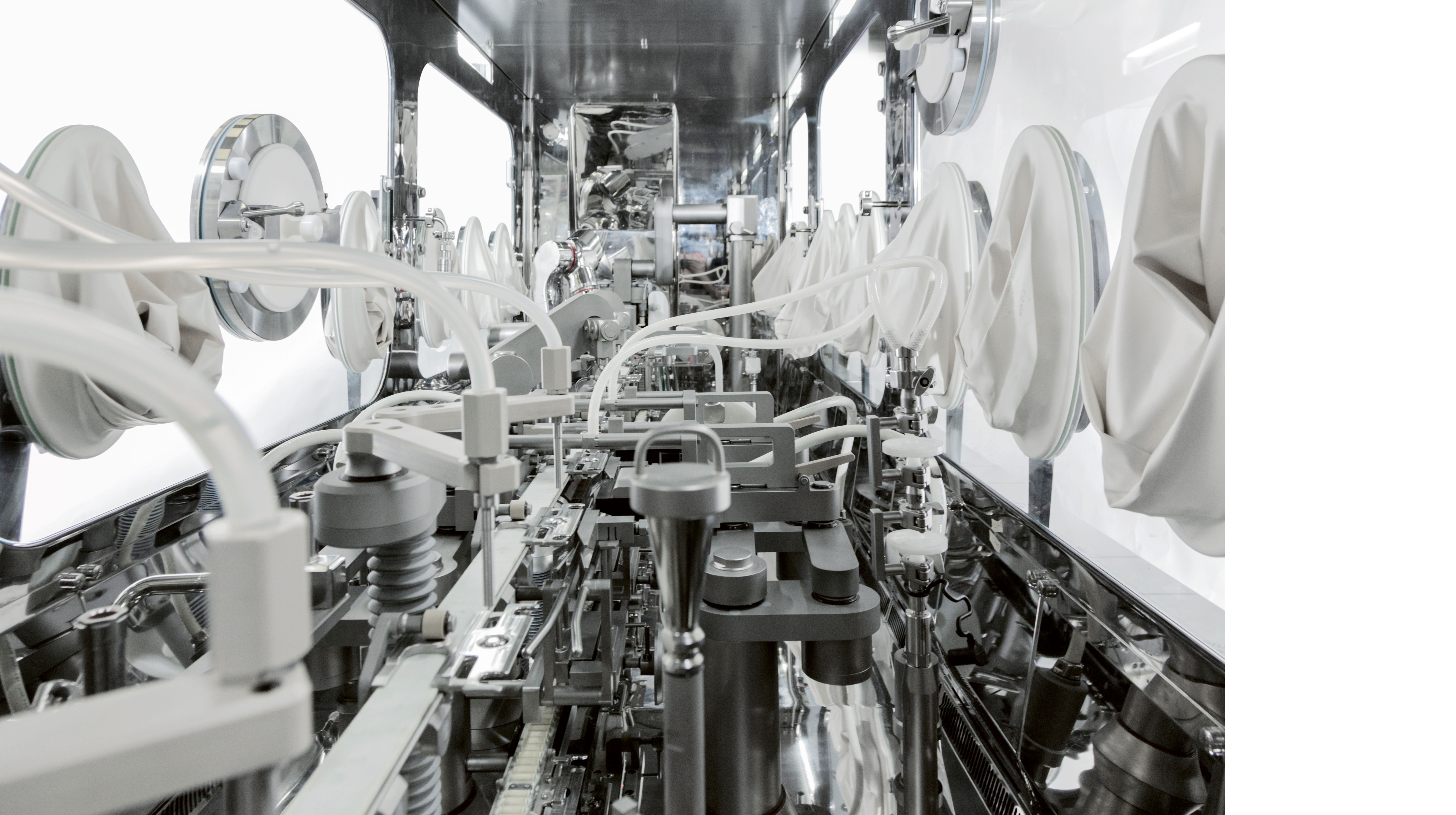
Isolators are clean air devices providing complete separation between an aseptic process (hazardous/non-hazardous), the technical personnel, and the surrounding work environment. Isolators are generally used in applications requiring a high degree of protection from external elements or contaminants, and they can serve as alternatives to sophisticated cleanrooms.
Isolators typically feature built-in air filtration systems capable of significantly lowering the particle count in an enclosed area. The relatively compact size of the isolator's interior makes it easier to clean with gas or vapor sterilizing agents. Isolators can be configured to have either positive or negative pressure relative to the surrounding environment depending on the application. Positive pressure isolators provide product protection against contaminants, hence maintaining sterility; while negative pressure isolators, on the other hand, provide personnel and or environmental protection by containing the hazardous or toxic materials inside the isolator.
Aseptic Isolators are critical for the provision of an isolated ISO Class 5/Grade A environment required for the manufacture of sterile products and for carrying out aseptic processes. These types of isolators can carry out automated pressure hold tests, automated bio-decontamination, and continuous environmental monitoring to ensure the maintenance of the required condition.
Applications
- Cell Therapy/Bioprocessing/Cell
- Electronics/Semi-conductors Production
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- Research and Development
- Sterility Testing
Containment Isolators are often designed with a negatively pressured system for the containment of the environment used for processing hazardous products and highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs). This type of isolator is typically in turbulent airflow, capable of carrying out automated pressure hold test, with breach compensatory mechanism to prevent the escape of the hazardous product. In this type of system, operator protection is the priority
Applications
- HPAPIs and Potent Powder Handling
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- Research and Development
- Weighing and Dispensing of Powders/Excipients
Class III BSC-configured isolators are configured to operate as a Class III Biological Safety Cabinet. A Class III BSC is a closed-system airflow cabinet designed to provide protection from biohazards by maintaining negative pressure inside the cabinet and providing a rigid leak-tight physical barrier between the worker and the source of the biohazard.
Applications
- Cell Processing/Bioprocessing/Cell Cultures
- Laboratory containment for handling biological agents of up to level 4
- Research and Development
- Virus and Vaccine Production
Isolators are now being increasingly utilized for Pharmacy Compounding applications. In the United States Pharmacopeia, two (2) types of isolators are being described for this process:
Compounding Aseptic Isolator (CAI) - provides a safe and clean environment for compounding of non-hazardous, sterile drug preparations and IV admixtures in compliance with USP <797> criteria.
Compounding Aseptic Containment Isolator (CACI) - provides a safe and clean environment for compounding hazardous drug preparations in compliance with USP <797> and <800> criteria. It is suitable for work involving hazardous materials, antineoplastic, or cytotoxic compounding applications.
Applications
- Chemotherapy/Hazardous Drug Handling
- Cosmetics/Cosmeceuticals
- Research and Development
- Sterile/Aseptic Compounding
- TPN Formulation and Compounding
Cell Processing Isolator (CPI) is an integrated system that combines several types of equipment into one isolation technology. It is designed to isolate the process to ensure operator safety without compromising product quality. It also provides a sterile ISO Class 5/Grade A environment that is required to carry out aseptic processes.
Applications
- Allogenic Cell Therapy
- Aseptic Processing
- Autologous Cell Therapy
- Cell Banking
- Cell Processing
- cGMP Manufacturing
- Monoclonal Antibody Production
- Vaccine Research
- Virus Production